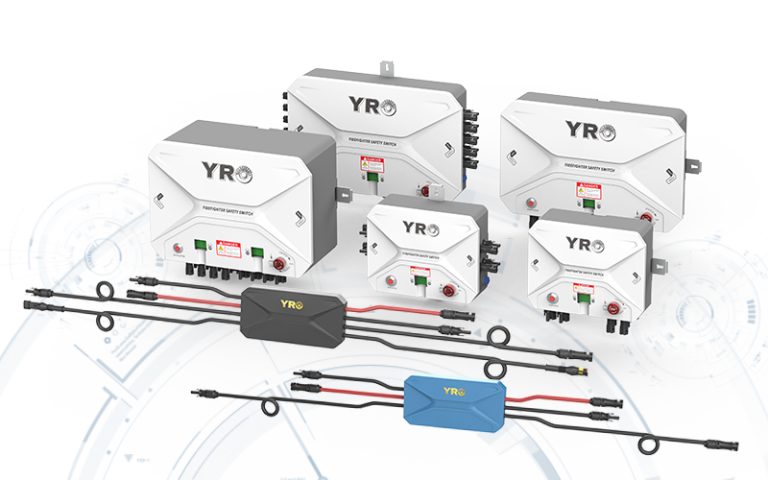
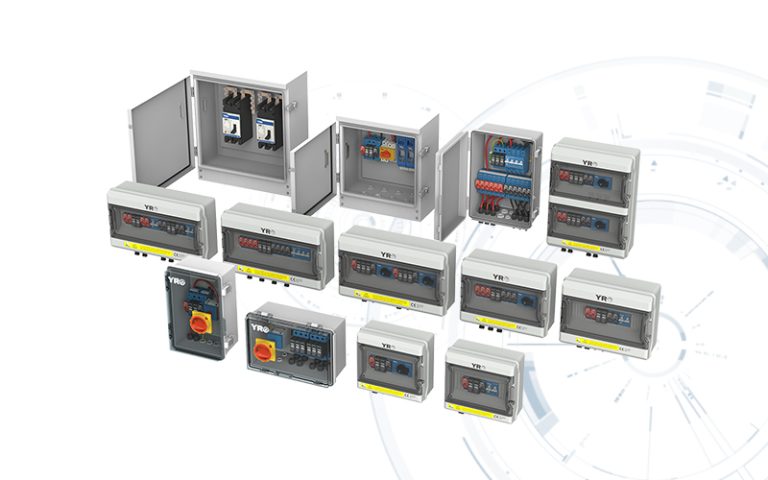
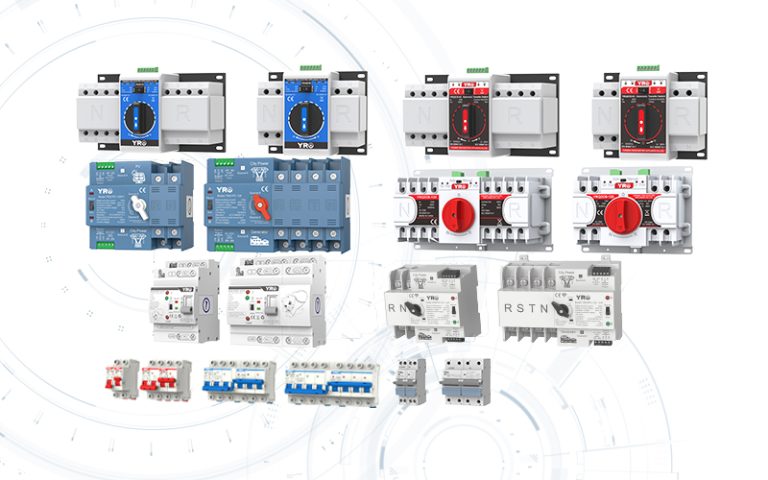
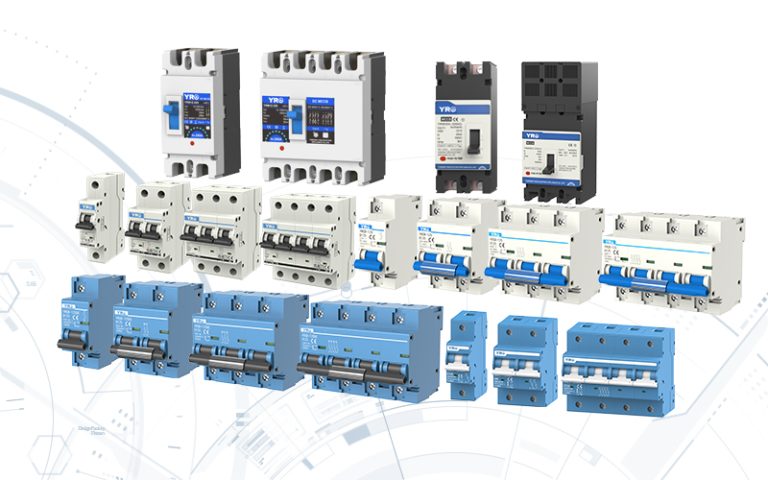
In modern photovoltaic (PV) systems, safety, efficiency, and reliability depend heavily on the right protective components. From Rapid Shutdown Devices to PV Combiner Box DC Circuit Breakers, Fuses, Surge Protectors, Isolator Switches, and Solar Connectors, each device plays a critical role in preventing equipment damage and ensuring smooth operation.
Understanding what is an isolator, the function of circuit breakers, and their differences is essential for procurement professionals and system designers looking to optimize PV systems while safeguarding costly solar assets. Lets explore isolator switch and circuit breaker together to see thier key differences in Photovoltaic System.
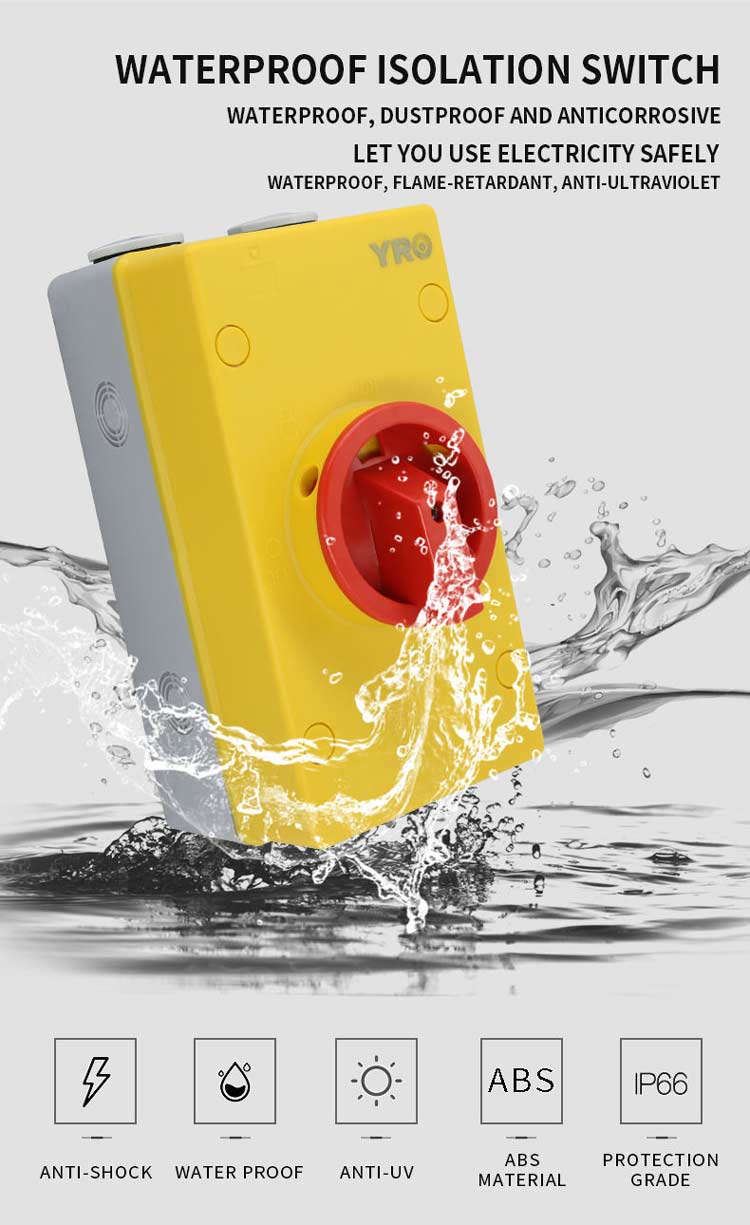
1. Understanding Isolator Switches
1-1 Definition and Purpose
An isolator switch is a manual device that completely disconnects electrical circuits. It is primarily used for maintenance or emergency situations, providing visible and reliable isolation to ensure safety for technicians and equipment.
1-2 Functionality
-
Manual operation: Requires physical actuation.
-
Off-load operation only: Cannot interrupt current under load.
-
Safety assurance: Confirms that sections of the PV system are completely isolated before maintenance.
1-3 Application in PV Systems
-
Disconnecting strings of solar panels during inspection.
-
Ensuring integration with Rapid Shutdown Devices for emergency scenarios.
-
Working alongside Solar Connectors and PV Combiner Boxes for a safe maintenance workflow.
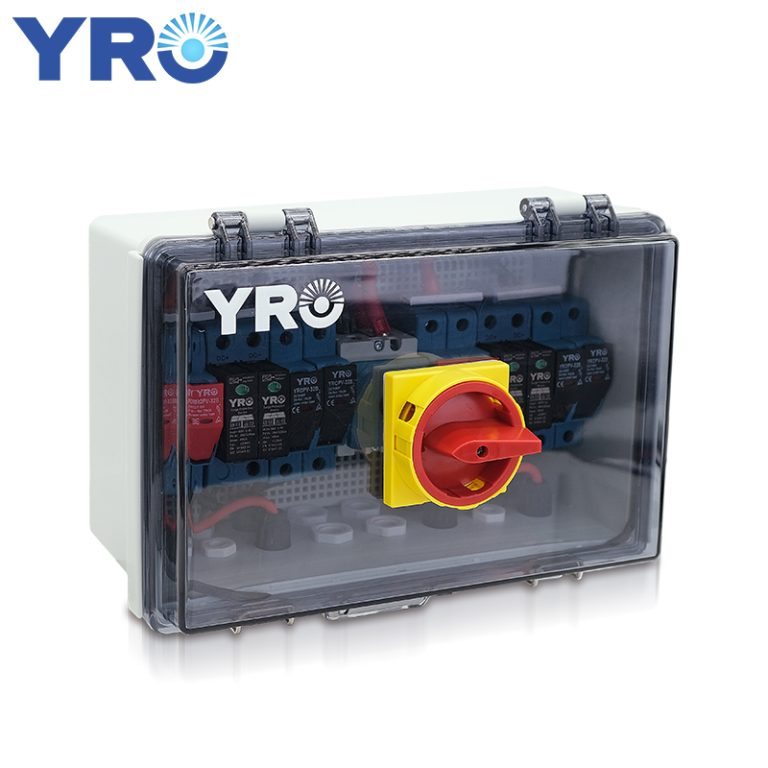
3. Understanding Circuit Breakers
3-1 Definition and Purpose
A circuit breaker is an automatic protective device that interrupts current flow during overloads, short circuits, or other faults. Unlike isolators, circuit breakers protect PV systems in real-time, ensuring both equipment safety and system reliability.
3-2 Functionality
-
Automatic operation: Triggers during fault conditions.
-
On-load capability: Can interrupt current without manual intervention.
-
Arc suppression: Reduces risk during high-current interruption.
-
Rated for specific voltage and current to match PV system requirements.
3-3 Application in PV Systems
-
Protecting inverters, PV modules, and electrical infrastructure from damage.
-
Integrating with Fuses and Surge Protectors to provide multi-layered protection.
-
Typical applications include PV Combiner Box DC Circuit Breakers and Circuit Breakers in Substations.
4. Key Differences Between Isolator Switch and Circuit Breaker
| Feature | Isolator Switch | Circuit Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Manual | Automatic |
| Current Handling | Off-load only | On-load and fault conditions |
| Safety Mechanism | Visible disconnection | Arc suppression & overcurrent protection |
| Primary Use | Maintenance isolation | System protection during faults |
| PV System Placement | PV Combiner Box, Solar Strings | Substations, Fuses, Surge Protectors |
4-1 Operational Mechanism
- Isolator Switch: Operated manually, requiring physical intervention. Commonly used during inspections, repairs, or emergency maintenance.
- Circuit Breaker: Operates automatically in response to overload, short circuits, or faults. No manual intervention is needed to trip the circuit, making it crucial for continuous system protection.
4-2 Current Handling
-
Isolator Switch: Functions in off-load conditions only; cannot safely interrupt current under load.
-
Circuit Breaker: Designed for on-load and fault conditions, capable of breaking live current with arc suppression technology.
4-3 Safety Considerations
-
Isolator Switch: Provides visible disconnection, giving maintenance staff clear confirmation that a circuit is fully isolated.
-
Circuit Breaker: Focuses on arc suppression, tripping mechanisms, and automatic fault interruption, ensuring that dangerous current flows are stopped immediately.
4-4 System Integration
-
Isolator Switch: Commonly integrated into PV combiner boxes and works alongside solar connectors for safe string isolation.
-
Circuit Breaker: Typically installed in combiner boxes and substations, often paired with fuses and surge protectors for layered protection.
4-5 Performance in Extreme Conditions
-
Isolator Switch: Performs reliably under standard PV conditions but is not designed for sudden high-current faults.
-
Circuit Breaker: Built to withstand extreme fault conditions such as short circuits, lightning surges, and grid disturbances, making it indispensable for long-term system reliability.
5. Why Choosing the Right Protective Component Matters
5-1 System Reliability
High-quality protective components minimize downtime and safeguard critical assets such as PV modules, inverters, and cabling.
-
Isolator switches ensure that maintenance can be conducted safely without risking equipment damage.
-
Circuit breakers provide automatic protection against overloads and short circuits, reducing the likelihood of catastrophic failures.
-
Reliable fuses and surge protectors prevent damage from transient voltages and lightning strikes.
Procurement Insight: Investing in certified protective components reduces unexpected failures, improves energy yield, and builds trust with end users.
5-2 Safety Compliance
Compliance is not optional in modern PV systems—it is a mandatory requirement under global and regional standards.
-
Devices must meet IEC standards (such as IEC 60947 for low-voltage switchgear and IEC 60364 for electrical installations).
-
Local electrical regulations often mandate the use of Rapid Shutdown Devices in rooftop PV systems to ensure firefighter safety.
-
Isolator switches provide visible disconnection, which is often required under occupational safety standards.
Procurement Insight: Selecting compliant devices not only avoids legal risks but also enhances brand credibility when delivering PV projects.
5-3 Procurement Considerations
For procurement professionals, compatibility and integration are key. Choosing a unified set of protective components from a reliable supplier simplifies both installation and long-term maintenance.
-
Rapid Shutdown Devices integrate seamlessly with isolators and circuit breakers.
-
PV Combiner Box DC Circuit Breakers reduce wiring complexity and improve reliability.
-
Solar connectors designed for high-voltage PV applications ensure consistent performance in harsh conditions.
Procurement Insight: Selecting components from a single trusted source ensures interoperability, reduces installation errors, and streamlines supply chain management.
5-4 Cost Efficiency
While premium protective devices may appear to have a higher initial cost, they deliver substantial long-term financial benefits.
-
Reduced repair and replacement costs.
-
Lower risk of warranty claims and insurance issues.
-
Increased return on investment (ROI) due to reduced downtime and higher energy yield.
Procurement Insight: Spending slightly more on high-quality isolator switches, circuit breakers, and surge protectors leads to significant savings over the system’s 20–25 year lifecycle.
| Component | Key Benefits | Cost Considerations | ROI / Value for PV Installations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isolator Switch | – Provides safe manual disconnection for maintenance – Visible isolation ensures technician safety – Reduces risk of accidental electrical contact | – Moderate upfront cost – Requires manual operation | – Minimizes maintenance accidents – Ensures compliance with safety standards – Extends equipment lifespan |
| Circuit Breaker | – Automatic protection against overload and short circuits – Arc suppression for high-current safety – On-load operation ensures system continuity | – Higher upfront cost than isolator – May require periodic testing and maintenance | – Prevents equipment damage and system downtime – Reduces repair and replacement costs – Enhances long-term system reliability |
| Combined Use | – Isolator + Circuit Breaker provides both manual and automatic protection – Optimized PV system safety – Integrates with fuses, surge protectors, and combiner boxes | – Higher initial investment | – Maximized safety, reliability, and compliance – Long-term cost savings through reduced failures – Supports safe and efficient maintenance operations |
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between isolator switches and circuit breakers is essential for building safe, efficient, and reliable PV systems. Isolators provide manual, visible disconnection for maintenance, while circuit breakers automatically protect against overloads and faults.
By choosing high-quality protective components—including Rapid Shutdown Devices, PV Combiner Box DC Circuit Breakers, Fuses, Surge Protectors, Isolator Switches, and Solar Connectors—procurement professionals can enhance system safety, optimize performance, and reduce long-term costs.
Explore our comprehensive portfolio of PV system protective components today. Request a consultation or quote to ensure your business is fully protected with reliable, industry-compliant solutions.